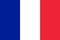
Few people know that the use of vinegar can solve the rather complex medical problem of getting rid of nail fungus. Thanks to the availability of table vinegar (9% acidic solution) and even vinegar essence (70% acidic solution), which can be purchased at a hardware store or market, there are many ways to treatfoot fungus using this product.
Of course, self-medication with vinegar should be carried out only if the disease has not progressed to an advanced form, and it is advisable to combine it with specially developed drugs. However, when there is an urgent need to treat nail fungus and you do not have the money or time to consult a doctor or undergo drug treatment, you can use vinegar yourself, the main thingis to follow the appropriate safety rules.
Features of using vinegar to treat mushrooms

The main effect of using vinegar is the creation of an acidic environment in the area of fungal infection, which prevents the growth of hyphae and the spread of spores. Little by little, the fungus, left without access to new sources of nutrients, dies and the absence of much more resistant spores prevents the possibility of a relapse of the disease.
At first glance, everything is very simple: how to destroy bacteria with an antiseptic. But in fact, the fungus turns out to be very tenacious, since its body is not on the surface of the nail or skin, but penetrates deep into the tissues. In this regard, a positive result from the treatment of oncomycosis should be expected only in the case of strict regularity of procedures, which will not give the parasite time to readjust and penetrate under the skin.
Before treating nail fungus, make sure that the concentration of acetic acid used matches that specified in the recipe. If a recipe mentions vinegar essence, it means a 70% solution, which should be dissolved or applied sporadically. Food or table vinegar contains 6 and 9% acid respectively. Neglecting this data can result in treatment ending in a chemical burn.
Apart from this point, there are no particular contraindications to vinegar treatment. Individual intolerance is very rare, but vinegar is such a common substance that patients are usually aware of this feature of the body. A burning sensation may very well occur during the first procedures, but it is normal and will subside over time. Otherwise, vinegar, if safety rules are followed, poses no threat to health.
Vinegar baths
Warm foot baths are considered an effective remedy for fungus; regular use allows you to get rid of onychomycosis at an early stage without additional medications. In addition, vinegar baths are an excellent prevention of fungal infections. The procedure requires lukewarm water, around 50°C, and a glass of table vinegar with a concentration of 9%. The water level in the pool should not be high, but only ankle-deep. The feet are immersed in the solution and kept there for 15 minutes.
Before the vinegar bath, it is advisable to carry out a complete pedicure procedure, including the removal of the affected areas of the nail plate and dead layers of the skin, calluses and corns of the feet, but without applying anydecorative coating on nails. If you cut and file your nails yourself, you should do so very carefully, as microdamage to the skin can contribute to the spread of a fungal infection.
Immediately after the vinegar bath, dry your feet with a towel and put on cotton socks. Repeat three times a week.
Vinegar Lotions
It is best to apply lotions to areas affected by fungus after vinegar baths. For this, pharmaceutical products and pure 9% vinegar are suitable, in which a cotton pad is moistened and applied to the nail for fifteen minutes.
A more complex recipe: a mixture of vodka or forty-degree medical alcohol, glycerin and 70% acetic acid in equal proportions, mix until smooth. A cotton swab dipped in the solution is held on the affected areas for fifteen minutes, after which cotton socks are put on. The duration of treatment is one week, if necessary, it can be repeated after a few days.
Vinegar-based ointments keep for a long time, they are more convenient to use than products with a liquid consistency. To prepare vinegar ointment, you need to take 70% acetic acid, dimethyl phthalate, glycerin and olive oil in a ratio of 2: 1: 1: 1, respectively. After thoroughly mixing all the ingredients, the ointment is ready for use.
To prevent the spread of a fungal infection and destroy its pathogens, you need to apply the ointment to the affected areas daily with a cotton swab, leave for 8-10 hours, then rinse with laundry soap. This recipe can be used not only to treat oncomycosis of toenails, but also affected nails.
Preventive measures against fungus consist of observing hygiene rules, especially in public places - bathhouse, swimming pool, bowling club. Choose comfortable shoes and socks made from natural materials, because poor circulation in the feet combined with high humidity creates the prerequisites for the development of onychomycosis (read also: onychomycosis - causes and prevention). Gym exercises, moderate physical activity and running can improve blood circulation and strengthen the immune system, making the body invulnerable to fungal and other infections.
Treating Toenail Fungus With Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is an effective remedy for onchomycosis, acting directly on the cause of the disease – dermatophyte fungi. Tea tree essential oil contains alpha-terpinene, alpha-phellandrene, limonene, sabinene, cineole and other substances that give it its antiseptic properties and anti-inflammatory effect.
Before using essential oil, it is necessary to carry out an allergy test - apply a little product to the skin of the wrist, if within 12 hours there is no irritation, redness ofrash or other reactions, the product can then be used for medicinal purposes. . Otherwise, it must be diluted to a safe concentration or this technique must be abandoned altogether.
Ways to Use Tea Tree Oil:
Foot baths with tea tree oil. Warm water is poured into a basin up to the level of the ankles, 15-20 drops of essential oil are added and the feet are kept there for twenty minutes, maintaining a high water temperature (45-50 °VS). The duration of treatment is two months, baths must be taken daily. During the treatment procedure, it is necessary to remove the affected areas of the nail plate using a file, nail clippers or scissors.
Apply oil to the nail plate. If you do not have a reaction to undiluted tea tree oil, in order to improve the effectiveness of the effect, it is applied in its pure form to the affected areas of the nail. First, the feet are steamed in warm water with the addition of laundry soap (for better dissolution, it can be grated). The oil is rubbed into the nail plate with a cotton swab twice a day, there is no need to rinse the product.
How to quickly cure toenail fungus?

The internal and external use of hydrogen peroxide for the treatment of infectious and other diseases was described by Professor Neumyvakin in a book written based on his personal experience. It mentions hydrogen peroxide as a preventative agent with antibacterial properties.
External use of hydrogen peroxide to treat fungal infections is carried out after spraying the feet in warm water with the addition of dissolved soda at the rate of one teaspoon per liter. When the nail plates become soft, pinch a small fragment of the affected area of \u200b\u200bthe nail using nail clippers and, after dipping it in a 3% solution of peroxide, apply it tothe nail plate. Leave on for 10 to 15 minutes on the nails or 40 minutes to an hour on the toes. Perform the procedure twice a day until the symptoms of the fungal infection disappear.
To reduce the evaporation of peroxide and increase the intensity of the effect, the nail plate with the lotion is wrapped in plastic film. After the exposure time has expired, rinse your toes and hands thoroughly under running water.
For therapeutic and prophylactic purposes, it is recommended to instill hydrogen peroxide into the nail cavity three times a day.
Hand and foot baths (depending on the location of the onychomycosis) with hydrogen peroxide give good results. Dilute 3% hydrogen peroxide in water at a temperature of 40-50 °C at the rate of two tablespoons per liter of water. The duration of the procedure is fifteen minutes, the frequency is twice a day for a week.
Instead of hydrogen peroxide in this recipe, you can use dead water with a negative redox potential, also called anolyte water. Anolyte Water is safe for sensitive skin, but has antiseptic properties that reduce the growth of fungus.
Effective treatment of advanced toenail fungus
This extreme method of treating fungal infections is used for severe damage to the nail plate, it should be used with caution so as not to damage the skin.
To get rid of fungus, the nail is treated with a rust neutralizer (this can be purchased at an auto parts store). This product contains phosphoric acid, which effectively destroys fungi, but if used carelessly, it can damage skin tissue. Therefore, when using it, it is necessary to observe safety precautions - work in a well-ventilated area, wear safety glasses and rubber gloves, avoiding contact of the product with skin and mucous membranes.
A safer way would be to use kerosene, which also has high penetrating power and a very powerful effect on the fungus.
Other folk remedies for toenail fungus
Complex treatment of toenail fungus using traditional recipes based on hydrogen peroxide allows you to destroy the fungus and permanently get rid of the unpleasant odor and other accompanying symptoms.
Two effective folk remedies for fungal infections:
Peroxide recipe 1. To prepare the healing mixture, you will need slaked soda (0. 5 cups), hot water (4 cups), 3% hydrogen peroxide (0. 25 cups) andhalf a cup of magnesium sulfate or Epsom salts. Mix all the ingredients thoroughly and pour in another quarter cup of vinegar. Soak a cotton swab with the resulting solution and attach it to the nail plate affected by the fungus using a bandage. The dressing must be renewed every ten hours, the duration of treatment is one month.
Peroxide recipe 2. The procedure for processing mushrooms according to this recipe includes three stages. First of all, you need to prepare a solution for treating nail and skin surfaces affected by the fungus - mix 3% vinegar and peroxide at a concentration of 3% in a ratio of 1: 1. This mixture sApply to feet while it sizzles. The second stage involves immersing fingers with fungal nail infection for half a minute in a weak solution of bleach in water, after which they are thoroughly washed under running water and wiped with atowel. Finally, tea tree oil mixed with petroleum jelly in equal proportions is applied to the nail plate. Wear warm socks or gloves (if this technique was used to treat nail oncomycosis). The duration of treatment is one week.
Novocaine lotion. Novocaine lotion is a very simple but effective folk remedy for treating fungus. Simply soak a piece of cotton with novocaine and apply it to the fungus overnight. Two of these lotions are enough to permanently eliminate the fungus.
Apricot resin tincture: pour 1 tablespoon of resin extracted from the tree with a glass of vodka, leave for three days. Lubricate the skin of the feet and nails with this solution. Shake before each use. It took us a month for processing; affected nails were cut as they peeled off and new healthy nails grew. After examination, the doctor confirmed recovery. I can also recommend using old, thickened sunflower oil in this case.
Garlic Applications: I took a clove of garlic, squeezed it using a garlic press, applied the mixture to the nail, covered it with cellophane andI wrapped it in a bandage or put it on the tip of a finger. I left the dressing on until morning; the first few days I felt a throbbing pain, like an abscess, but I had to endure it. I repeated the procedures daily and new nails grew.
Strong coffee. Few people know that ordinary but strong coffee is a very good folk remedy for treating fungus. Make yourself a stronger cup of coffee and simply dip your hands or feet into the cup, depending on where you have the fungus. It is best to perform this procedure in the evening, before going to bed. The fungus completely disappears after several evening procedures. At the same time, the skin becomes smooth and the pain quickly disappears.
Nail fungus in adults: symptoms, causes, treatment
In medicine, nail fungus is officially called onychomycosis. This is a fungal disease that affects the nail plates of the fingers or toes. According to the WHO, this is a fairly common disease. It occurs in approximately 27% of people and the pathology is diagnosed twice as often on the legs as on the arms. The problem of nail fungus is very delicate, since the unpleasant appearance of the affected plates causes the patient discomfort and hides them from others.
Symptoms and signs of nail fungus
Onychomycosis is very easy to recognize, since its signs on the nails cannot be ignored. First, the nail plates become dull and rough, losing their shiny shine. Then the nail turns dirty yellow, whitish or gray instead of pink. Then other characteristic symptoms of the fungus appear:
- increased plaque thickness;
- defects in the form of scratches, bends, irregularities and waves;
- delamination and crumbling of the plaque;
- unpleasant smell from the nails.
As a result, the nail is completely destroyed and even peels off, exposing the nail bed. The skin next to the patches turns red and is very itchy.
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Do not delay your consultation, contact a specialist as soon as possible.
Causes
The main cause of the development of fungal infections is the entry of a pathogen onto or into the human body. As a rule, these are microsporums, trichophytons and epidermophytons. It is these fungi that especially often cause onychomycosis.
When they enter the body, these fungi are localized on keratinized skin derivatives, that is to say nails and hair. This is explained by the parasites' diet, for which they use the fibrillar protein keratin, present in nails and hair.
The main cause of mycosis is infection with a pathogenic fungus. At the same time, many types of fungi are constantly present in the body, and their growth is usually inhibited by the immune system. As control decreases, the fungus begins to grow on the skin or tissues of internal organs. This often happens because of:
- a chronic illness that weakens the body;
- non-compliance with hygiene rules;
- insufficient or unbalanced diet;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- exposure to external factors that weaken the body - hypothermia, excess ultraviolet radiation, poisoning, radiation damage, etc.
- long-term use of antibiotics or certain other medications.
The only exception here is something called mycosis fungoides, which is not a fungal disease. It is an oncological tumor pathology, based on the degeneration of T lymphocytes into a malignant form.
Routes of infection
The risk of being infected by a fungus is particularly high in public places with high humidity. These include saunas, swimming pools, gyms, public baths, etc. The most common routes of infection:
- direct contact with an infected person. Here, the fungus moves from its habitat to healthy areas, thereby causing infection;
- domestic manner. In this case, infection occurs when using the patient's personal belongings: shoes, personal hygiene items, etc.
There are many ways to become infected with fungal diseases. Most often this happens:
- in direct contact with affected areas of another person's skin;
- when sharing towels, slippers, personal hygiene items;
- via a contaminated manicure instrument;
- by contaminated clothing and shoes;
- through the ground, particularly in the presence of skin microtrauma;
- in contact with domestic animals.
Skin fungus often develops in people who use swimming pools, saunas, showers in sports clubs, etc. Infection is more likely if the person's immune system is functioning poorly.
Risk factors
The incidence of onychomycosis increases from the age of 60. Currently, the probability of developing such an infection is 60%, which is explained by a slowdown in metabolism, especially in the distal (distant) parts of the body, such as the fingers and toes.
Other risk factors for developing nail fungus include:
- diabetes;
- varicose veins;
- injuries to nails and adjacent tissues;
- HIV and other immunodeficiency problems;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- weakened immune system;
- vascular and skin diseases, dermatitis, diaper rash;
- blood supply disorders to the extremities;
- insufficient hygiene.
Complications
In a simple course, the disease causes traditional symptoms of the fungus, causing only severe discomfort in a person. But if left untreated, onychomycosis can lead to complications. Most often they manifest themselves with the addition of a bacterial infection.
Sometimes onychomycosis is very acute with the appearance of blisters, ulcerations and oozing areas on the skin near the nail. In severe cases, the disease takes a generalized form. This means that the nail fungus spreads to internal organs and systems, and the patient will then need to be hospitalized urgently.
When to consult a doctor
Many who have encountered onychomycosis know that the disease develops slowly and is incredibly difficult to treat. This is why it is very important to consult a doctor as soon as the first signs of the disease appear. A dermatologist treats nail onychomycosis in clinic. The specialist will provide you with competent assistance and guide you until complete recovery.
Prepare to see the doctor
Before consulting a dermatologist, it is important not to treat the affected areas of the nails with anything, i. e. do not use medications, including iodine and brilliant green. You should also avoid the use of creams and ointments against fungus. At your appointment, you must have all previously performed tests, including those for other illnesses. The affected nails should not be cut 3 to 4 days before the consultation.
Diagnosis of nail fungus
First of all, the patient is sent for microscopy, which helps identify the presence of the pathogen. In the future, it will be necessary to determine its type in order to select the appropriate treatment for toenail fungus. The professional clinic practices the most modern and common methods for diagnosing onychomycosis:
- cultural examination of a biological sample of affected tissue. To do this, it is placed in an artificial nutrient medium, where the pathogen is cultivated in order to determine its type;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method for detecting pathogenic DNA in a sample of affected tissue.
As part of the diagnosis of mycoses, studies on scrapings of skin and nail formations, sputum, blood, hair, scrapings of mucous membranes, stools and other biomaterials can be carried out, depending on the type and locationof the lesion. For skin diseases, the following operations are usually performed:
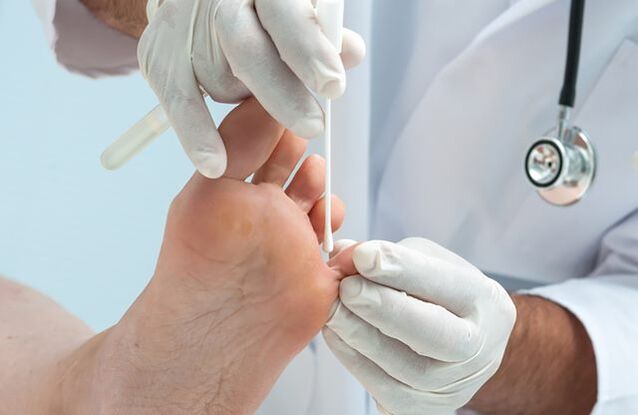
- dermatoscopy - examination of affected areas of skin, hair or nails to identify characteristic signs;
- microscopic examination of scrapings to detect fungal mycelium;
- bacterial culture on nutrient medium, which allows you to identify not only the type of fungus, but also the optimal drug for treatment;
- serological blood test;
- PCR test to detect the fungal genome.
Some types of fungi are quite easily diagnosed using UV radiation generated using a Wood's lamp.
Along with determining the type of fungus, the patient undergoes a general examination to identify the cause of the weakening of immunity that led to the infection.
Treatment
At an early stage of the disease, local treatment is usually prescribed, which consists of the use of creams and ointments with an antifungal effect.
Antiseptic solutions are also used as external remedies for nail fungus. In addition to effective remedies for nail onychomycosis, antihistamines and desensitizing drugs are prescribed to relieve swelling, inflammation and sensitivity.
If the nail is completely affected by the fungus and drug treatment does not give positive results, then the plaque is subject to surgical removal. In addition, in the total form of onychomycosis, antimycotic drugs are prescribed orally in the form of tablets, which have a systemic effect on the body.
When choosing drugs, the dermatologist must take into account the individual sensitivity of the pathogen to a particular drug. Independent use of certain drugs often does not bring the desired result, because before starting treatment it is necessary to determine the type of causative agent of the disease. For some fungal infections, the patient's diet becomes important. So, when treating yeast and mold, it is necessary to exclude foods containing fast carbohydrates (candies, flour products), fermented foods, alcohol and potatoes.
Home remedies
Before using home remedies, you should consult your doctor. With permission, you can use the following recipes:
- iodine. Before use, the feet should be steamed, washed with laundry soap, and then the affected areas of the nail plates should be removed. Then treat the nails and skin between the fingers with iodine, soak them in a bath with soda solution for 20-30 minutes and dry thoroughly;
- vinegar. For 3 liters of water, take 1 tbsp. apple cider vinegar and add a little potassium permanganate. Soak your feet in the bath for 20 to 30 minutes, then dry them thoroughly;
- hydrogen peroxide. After thoroughly steaming your feet, remove the affected areas from the nail plates. Place cotton pads soaked in hydrogen peroxide on top, wrap them with a bandage and leave for half an hour.
Prevention
To prevent the development of onychomycosis, it is necessary to exclude the negative effects of risk factors on the body:
- treat systemic diseases in a timely manner;
- do not wear someone else's shoes;
- carry slates in the pool and sauna;
- change socks daily and follow the rules of personal hygiene;
- do not wear wet shoes - dry them thoroughly;
- Avoid direct contact with potential carriers of the fungus.